When maximizing your CPU’s performance, understanding how to manage your core ratio can make a significant difference.
CPU Core Ratio Sync All Cores or Auto refers to settings where all CPU cores operate at the same frequency (Sync All Cores) or automatically adjust based on workload (Auto), balancing performance and efficiency.
This article will guide you through adjusting your CPU core ratio settings, explaining when and why you might want to sync or leave all cores on auto.
Understanding CPU Core Ratio Sync All Cores or Auto
The CPU Core Ratio controls how your CPU’s cores work together. Sync All Cores makes all cores run at the same speed, providing stable performance.
Auto lets the CPU adjust each core’s speed based on the workload. If your system is running heavy tasks, syncing all cores helps performance.
For lighter tasks, Autosaves power and reduces heat. The choice depends on whether you need maximum performance or efficiency.
1. The Difference Between All Cores and Auto
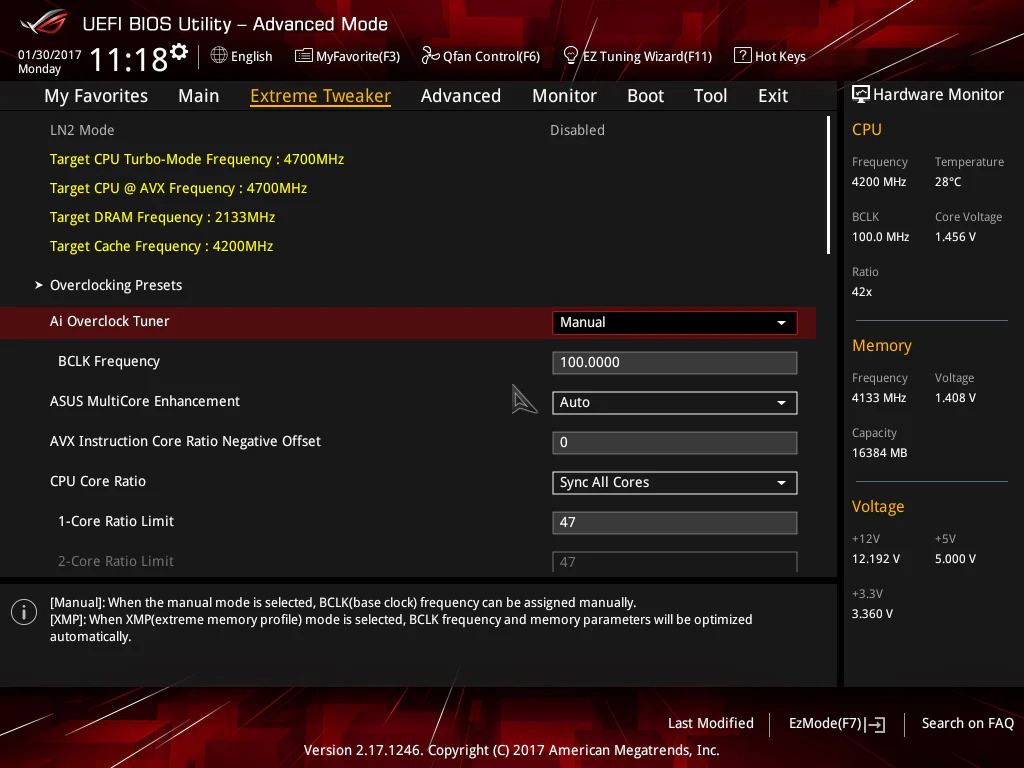
Sync All Cores means all your CPU cores work at the same speed. This is useful for tasks needing constant, high performance, like gaming or video editing. Auto, on the other hand, adjusts the speed of each core based on how much work is needed.
It’s more energy-efficient and reduces heat when your system isn’t under heavy load. If you want to save power and heat, choose Auto. For performance-heavy tasks, Sync All Cores is better.
2. All Cores Mode – When and Why to Use
All Cores Mode is great when you need consistent and strong performance. This is useful for gaming, video editing, or 3D rendering, where your CPU must work hard.
With all cores running at the same speed, your system can handle demanding tasks better. However, remember that this mode can increase power usage and heat. So, it’s best used when you want the best performance and have a good cooling system.
A. Steps to Enable All Cores Mode
- Restart your computer and press the BIOS key (usually Del or F2) during startup to enter the settings.
- In the BIOS menu, navigate to CPU Settings or Advanced Options. The exact location may vary depending on your motherboard.
- Look for the CPU Core Ratio Sync setting.
- Select All Cores from the options available.
- Save the changes and exit the BIOS by selecting the appropriate option (usually F10 or Save & Exit).
- Your system will restart, and all CPU cores will run at the same speed for consistent performance.
3. Auto Mode – When and Why to Use
Auto Mode is ideal for your system to run efficiently and quietly. It allows the CPU to adjust its core speeds depending on the workload.
For everyday tasks like browsing the web, watching videos, or light gaming, Auto Mode helps save energy and reduce heat.
It’s a good choice if you don’t need maximum performance all the time and want your computer to be more power-efficient. This way, your system runs cooler and quieter without wasting resources.
A. Steps to Enable Auto Mode
Enabling Auto Mode is similar to the process for enabling All Cores mode:
- Restart your PC and press the BIOS/UEFI key during startup.
- Go to CPU Settings or Advanced Options in the BIOS.
- Find the CPU Core Ratio Sync option.
- Select Auto.
- Save the changes and exit BIOS.
Once activated, the CPU will adjust its performance dynamically based on the tasks at hand, providing an optimal balance of power and efficiency.
Fine-Tuning Performance with CPU Core Ratio Sync
Fine-tuning your CPU with Core Ratio Sync gives you more control over how your CPU cores work. You can adjust each core’s speed to match your needs, whether you want to prioritize one core for heavy tasks or balance all cores for efficiency.
This flexibility is useful for gamers and professionals who need extra performance. However, be cautious when making changes to avoid overheating or instability. Always monitor your CPU’s temperature to ensure it’s running safely and efficiently.
1. Overclocking Considerations
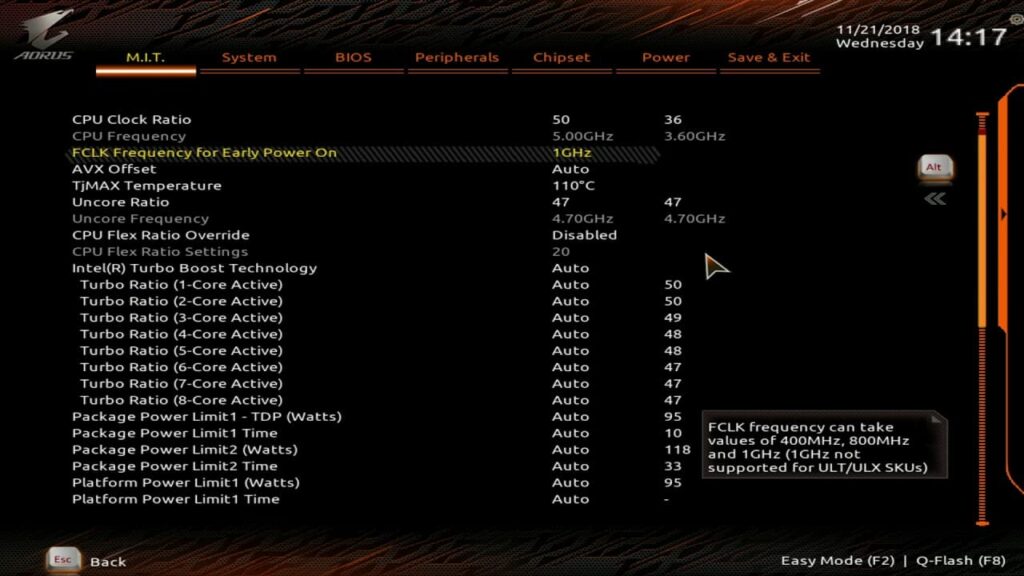
Overclocking your CPU can give you more power but comes with risks. Pushing your CPU beyond its default limits can increase performance and raise heat and power consumption. If you enable “All Cores” mode, ensure all cores run at the boosted speed for stability.
Overclocking can shorten the CPU’s lifespan if not done carefully. Ensure you have a strong cooling system, and always follow the manufacturer’s guidelines to prevent damage to your system.
Performance Implications
The choice between “Auto,” “Sync All Cores,” and “Per Core” settings can significantly impact system performance and behavior:
- Auto Mode: Offers a balanced approach, allowing the processor to adjust core frequencies based on workload demands dynamically. This mode is energy-efficient and suitable for general use cases.
- Sync All Cores: Ensures all cores run at the same elevated frequency, which can enhance performance in multi-threaded applications. However, it may lead to increased power consumption and heat output.
- Per Core: Provides the flexibility to optimize individual core frequencies, catering to specific performance needs or thermal considerations.
Considerations and Recommendations
When deciding on the appropriate CPU core ratio setting, consider the following:
- Workload Type: For tasks that benefit from high single-core performance, such as specific gaming scenarios, “Auto” or “Per Core” settings might be advantageous. For heavily multi-threaded applications, “Sync All Cores” could perform better.
- Thermal Management: Elevated core frequencies result in higher heat output. Ensure your cooling solution can handle the increased thermal load, especially when using “Sync All Cores.”
- System Stability: Not all cores are identical; some may not sustain higher frequencies reliably. Testing system stability when configuring these settings is essential to prevent crashes or data corruption.
- Power Consumption: Higher frequencies lead to increased power draw. Be mindful of your system’s power supply capacity and overall energy consumption.
Optimizing Your CPU for Efficiency and Performance
Balancing speed and energy use to get the best out of your CPU. “All Cores” mode provides steady, high performance if you’re gaming or editing videos.
On the other hand, “Auto” mode adjusts the CPU speed based on what you’re doing, saving power and keeping your system cool during lighter tasks.
Ensure your cooling system is up to the task, especially if using “All Cores.” Regularly clean your PC, update your BIOS, and use monitoring tools to keep everything running smoothly.
CPU Core Ratio Sync All Cores Or Auto Windows 11
In Windows 11, “All Cores” mode ensures consistent speed for heavy tasks, while “Auto” adjusts performance based on workload. You can choose the BIOS settings to optimize your CPU for either power or efficiency.
CPU Core Ratio Sync All Cores Or Auto Windows 10
Windows 10 works similarly to Windows 11. “All Cores” mode is ideal for demanding tasks like rendering, while “Auto” adjusts the CPU’s speed to balance power and energy efficiency. Both settings are customizable in BIOS.
CPU Core Ratio Sync All Cores Or Auto Gaming
“All Cores” mode provides steady gaming performance, making it perfect for high-demand games. However, “Auto” can dynamically adjust speeds, saving power during less intense moments. Choose the setting based on your game’s needs and cooling capacity.
13900k Sync All Cores
The Intel i9-13900k benefits from “All Cores” mode for demanding tasks like 4K gaming or rendering. This setting ensures all cores run at full speed for maximum performance, but it requires good cooling to avoid overheating.
How To Sync All Cores
To sync all cores, enter the BIOS during startup. Find the “CPU Core Ratio” setting, select “All Cores,” save your changes, and restart your system. Ensure proper cooling, as this increases power consumption and heat.
Sync All Cores 14900k
For the Intel 14900k, the “All Cores” mode ensures high performance during heavy tasks. Set this in BIOS for uniform core speeds, but ensure you have a strong cooling system to handle the increased power demands and prevent overheating.
All Core Ratio Limit
The All Core Ratio Limit defines the maximum speed at which all CPU cores can run. Increasing this limit can boost performance but may cause more heat. Adjust it carefully in BIOS and ensure your cooling system can handle it.
Core Ratio Setting In BIOS
The Core Ratio setting in BIOS controls how fast your CPU runs. “All Cores” sets all cores to the same speed, while “Auto” dynamically adjusts speeds. You can customize this setting based on your performance needs and system capabilities.
Synch All Cores or Auto
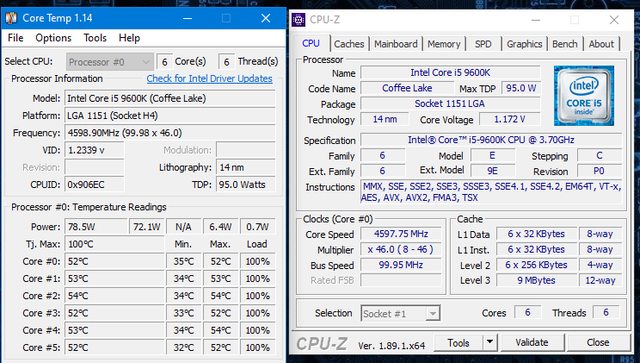
“Sync All Cores” offers uniform performance, perfect for tasks that need steady power. “Auto” dynamically adjusts speeds, optimizing energy use for lighter tasks. Choose based on whether you need constant performance or efficient power management.
8700k sync all cores vs per core overclocking
The 8700k performs well with both methods. “Sync All Cores” performs consistently, while “Per Core Overclocking” allows more control, boosting specific cores for higher speeds. Choose based on your cooling and performance needs.
Is Sync All Cores the same as Limit Core Ratio?
No, “Sync All Cores” sets all cores to the same speed, while “Limit Core Ratio” restricts how fast cores can go. The latter is about capping the maximum performance, whereas syncing all cores ensures even performance.
Is it better to sync all cores and should I let my CPU throttle down?
Syncing all cores provides stable performance and is ideal for heavy tasks. Allowing your CPU to throttle down can save power and reduce heat. It depends on your usage: sync for consistent performance, throttle for efficiency during light tasks.
Per Core vs All Core when overclocking?
“Per Core Overclocking” boosts individual cores for higher speeds, which is great for tasks needing peak performance on one core. “All Core” overclocking sets the same speed for all cores, offering steady performance for demanding workloads like gaming and rendering.
Sync all cores Asus ROG Strix z590z wifi
On the Asus ROG Strix Z590Z WiFi motherboard, syncing all cores in BIOS helps achieve stable performance for demanding tasks. Use this setting if you need all cores running at the same speed for consistent power during intensive processes.
Static all-core OC vs per-core OC for gaming latency?
Static all-core overclocking boosts all cores evenly, offering stable performance for gaming. Per-core overclocking boosts specific cores, potentially lowering latency in single-threaded tasks. Choose static OC for balanced power or per-core for peak gaming performance.
Is it ok to leave cpu ratio setting on auto when overclocking?
Leaving the CPU ratio on auto can work, but it won’t provide maximum performance. Auto settings adjust based on load, but manually setting the ratio during overclocking is usually preferred for better control and higher performance.
Is there any performance gain from syncing all CPU cores?
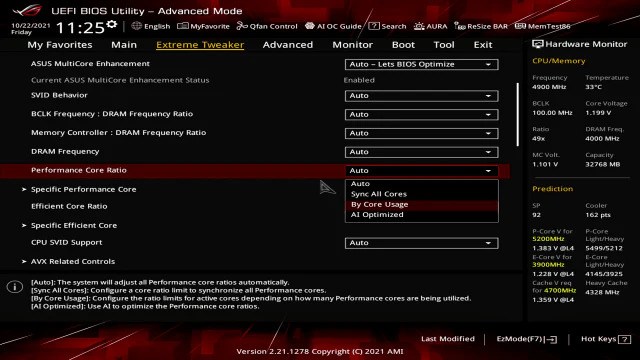
Yes, syncing all CPU cores can provide more consistent and stable performance. It ensures all cores run at the same speed, which is helpful for multi-threaded tasks, reducing bottlenecks and improving overall performance during heavy workloads.
Intel i7 8700 – Sync all cores in BIOS, will it boost a gaming performace?
Syncing all cores on the Intel i7 8700 can improve gaming performance, especially in CPU-intensive games. It ensures that all cores operate at the same speed, preventing bottlenecks and enhancing smooth gameplay during demanding moments.
Rendering + Gaming: Multicore Enhancement vs Sync All Cores vs Intel Specifications
Multicore enhancement increases performance by overclocking all cores while syncing all cores, which provides consistent speeds across all.
Intel’s specifications usually offer balanced performance, but enhancing multicore or syncing all cores can provide better results for rendering and gaming.
How to get all CPU cores on one clock speed but single core on a different one?
To achieve different speeds for all cores, use BIOS settings or software like Intel’s Extreme Tuning Utility. Set the base clock speed for all cores and manually adjust the single core’s clock to a higher speed for specific tasks.
FAQs
1. Should I sync all cores or not?
Syncing all cores is great for stability and consistency, especially for heavy tasks. But it may reduce power efficiency. Decide based on your needs.
2. Should CPU core ratio be auto?
Leaving the CPU core ratio on auto is fine for general use, but manual adjustments can give you more control and better performance.
3. Should I activate all cores on my CPU?
Activating all cores is helpful for tasks like gaming or rendering. It ensures maximum performance by utilizing the full potential of your CPU.
4. What is the best CPU ratio mode?
The best CPU ratio mode depends on your needs. “Auto” is simple, but “All Cores” or “Per Core” can provide better performance when manually adjusted.
5. Does using all cores increase FPS?
Using all cores can increase FPS in some games, especially multi-threading games. It ensures your CPU isn’t a bottleneck during intense moments.
6. How do I make sure all CPU cores are being used?
Check your CPU usage through Task Manager or use performance monitoring software. If all cores are active, it indicates they’re being fully utilized.
7. Is it bad to have too many CPU cores?
Too many cores aren’t bad, but they may not be fully utilized for everyday tasks. More cores are helpful for multitasking or specialized workloads.
8. Does adding more cores always increase performance?
More cores can improve performance in multi-threaded applications but not always in single-threaded tasks. It depends on the software and workload you’re using.
9. Is it better to have more cores and threads in a CPU?
More cores and threads are better for multitasking and demanding applications like video editing or gaming. For simple tasks, fewer cores may suffice.
10. Does Windows use all cores by default?
Yes, Windows uses all available cores by default. However, certain applications or power settings may limit core usage to save power or manage heat.
Conclusion
In conclusion, choosing between “Sync All Cores” and “Auto” depends on your needs. Syncing all cores offers stable performance for demanding tasks, while Auto optimizes efficiency for lighter workloads. Tailor your settings for the best balance of power and performance.