When you power your computer, several processes ensure everything runs smoothly. One of the first crucial stages is “Pre-Memory CPU Initialization.”
Pre-memory CPU initialization starts when your computer powers up. It prepares the CPU and memory components, ensuring smooth system operation, preventing errors, and optimizing performance for an efficient boot process.
In this article, we’ll dive into pre-memory CPU initialization and why it’s so important for your computer’s health.
The Importance of Pre-memory CPU Initialization
1. Overview of Pre-memory CPU Initialization
Before a computer fully starts, the CPU goes through several checks and setups in a phase called pre-memory initialization.
This process ensures that the CPU and memory work well together before loading the rest of the system. It includes checking the CPU’s cache, setting up memory controllers, enabling important system features, and ensuring everything is stable.
Without proper pre-memory initialization, your PC might show errors, freeze, or fail to start. Understanding this process can help troubleshoot motherboard issues and keep your computer running smoothly.
A. Cache Configuration
The CPU cache is like a super-fast memory that stores important data so the processor can access it quickly.
During pre-memory initialization, the system sets up the cache to work efficiently. If this step doesn’t happen correctly, your computer might slow down or show errors.
A properly configured cache helps speed up your system by reducing the CPU’s time to fetch data from RAM. This step ensures that your computer runs smoothly and efficiently immediately.
B. Memory Controller Initialization
The memory controller manages how data moves between the CPU and RAM. During pre-memory initialization, the system checks the installed memory, sets timings, and ensures RAM is ready.
If this step fails, your computer might not detect the memory properly or could show errors. A successful memory controller setup means your PC will run faster and more reliably, preventing crashes or slow performance.
C. System Management Mode (SMM) Initialization
System Management Mode (SMM) is a special mode that helps the CPU handle important background tasks like power management and security. During pre-memory initialization, SMM is set up to ensure these functions work correctly.
This step is important for protecting your system from overheating, managing laptop battery life, and preventing unauthorized access. Your PC might have power issues or security vulnerabilities if this setup fails.
2. CPU Features and Capabilities Initialization
Modern CPUs have many built-in features, like multi-threading and turbo boost, to improve performance. During pre-memory initialization, the system enables these features, ensuring your processor runs efficiently.
If this step fails, your CPU might not work fully, and you could experience slow performance. A proper setup ensures that all the processor’s abilities are used, helping your computer run faster and handle tasks better.
A. Virtualization Support Initialization
Virtualization allows you to run multiple operating systems on the same computer using software like VMware or VirtualBox.
During pre-memory initialization, the CPU checks if virtualization is enabled. If this step isn’t completed, you might be unable to use virtual machines properly.
Ensuring that virtualization is set up correctly helps improve performance and allows advanced users to run multiple environments efficiently.
B. Power Management Features Initialization
Your CPU adjusts its power use based on how much work it’s doing. This helps save electricity and reduces heat.
During pre-memory initialization, the system activates power-saving features like low-power states and dynamic voltage scaling.
If this step fails, your computer may use too much power, overheat, or drain battery life quickly. A proper setup ensures your CPU balances power use and performance effectively.
C. Performance Settings Initialization

The CPU can be tuned for better performance by adjusting clock speeds and core usage. During pre-memory initialization, the system configures these settings to match your hardware’s capabilities.
If this step isn’t completed correctly, your computer might run slower than expected or become unstable. Ensuring optimized settings helps your system handle demanding tasks smoothly while maintaining stability.
D. Security Features Initialization
Modern CPUs include security features like Secure Boot and hardware-based encryption to protect against malware and hacking.
During pre-memory initialization, these features are activated to keep your system safe. If this step fails, your computer might be more vulnerable to security threats.
A successful security setup ensures that your data stays protected and your system is secure from the moment it starts.
3. The Significance of Pre-memory CPU Initialization
Pre-memory CPU initialization is vital to the boot process, which ensures all critical components work correctly.
Before the system loads, it checks and configures the CPU, memory, power settings, and security features. You might see error codes, system crashes, or failed startups if this step fails.
A smooth pre-memory initialization ensures better performance, system stability, and security. Understanding this process can help you fix startup problems and improve your PC’s reliability.
Common Error Codes Associated with Pre-Memory Initialization
During the boot process, especially in the pre-memory initialization phase, various error codes may be encountered, indicating specific issues. Understanding these codes can aid in diagnosing and resolving boot problems. Some standard error codes include:
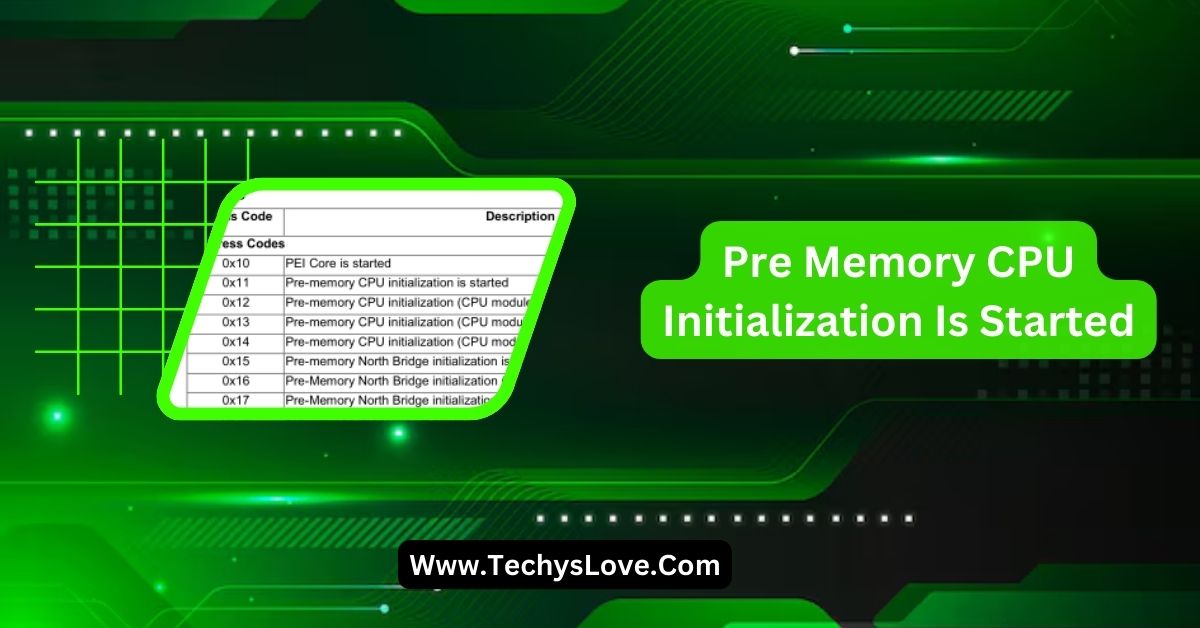
- Q-Code 14: Indicates that pre-memory CPU initialization has started. If the system halts at this code, it may suggest CPU initialization or compatibility issues.
- Q-Code 15: Signifies that pre-memory System Agent initialization has started. Halting at this code could point to problems with the System Agent, which manages communication between the CPU, memory, and other components.
- Q-Code 19: Denotes that pre-memory South Bridge initialization has started. Issues here may relate to the South Bridge chipset, which manages I/O functions.
These codes are typically displayed on a motherboard’s debug LED display and can vary between manufacturers. Consulting the motherboard’s manual or manufacturer’s website can provide specific information about these codes.
Troubleshooting Issues During Pre-Memory CPU Initialization
Encountering issues during the pre-memory CPU initialization phase can be challenging. However, systematic troubleshooting can help identify and resolve these problems. Here are some steps to consider:
- Check Hardware Connections: Ensure all components, especially the CPU and memory modules, are correctly seated and connected.
- Inspect for Physical Damage: Look for signs of damage on the motherboard, CPU socket, and other components.
- Update BIOS/UEFI Firmware: Outdated firmware can cause compatibility issues. Updating to the latest version can resolve known bugs and improve system stability.
- Test with Minimal Hardware Configuration: Remove non-essential components and peripherals to determine if they are causing conflicts.
- Verify Component Compatibility: Ensure that all hardware components are compatible with each other and the motherboard.
- Reset BIOS/UEFI Settings: Resetting to default settings can resolve misconfigurations that may hinder the boot process.
- Consult Manufacturer Support: If issues persist, reaching out to the motherboard or system manufacturer can provide additional guidance.
Pre-memory CPU Initialization Process
Before your computer starts, the CPU undergoes a pre-memory initialization process. This step sets up important hardware like the memory controller, cache, and power management.
The system checks if the CPU and RAM are working correctly. If anything goes wrong, your PC might show an error or fail to boot. A successful pre-memory initialization ensures a stable, fast, and efficient computer startup.
Pre-memory CPU Initialization Is Started Windows 11
In Windows 11, pre-memory CPU initialization prepares the processor and memory for startup. It ensures smooth communication between components, preventing boot errors. If this step fails, the system might freeze, show error codes, or fail to start properly.
CPU Post-Memory Initialization
After the memory is ready, post-memory CPU initialization configures advanced settings. This step fine-tunes the processor, enhances stability, and prepares the system for high-performance tasks.
A successful post-memory initialization ensures smooth operation, reducing crashes and improving overall system efficiency.
CPU Post Memory Initialization Windows 11
Windows 11 optimizes CPU post-memory initialization to improve boot speed and reliability. This process ensures proper power management configuration, virtualization, and security features. Updating the BIOS or checking memory modules can help fix the issue if errors occur.
15 Motherboard Code

The “15” motherboard code usually appears during early memory or CPU initialization. It often means the system is struggling to detect RAM. Reseating the memory sticks, checking compatibility, or updating the BIOS can help resolve this issue.
Q-Code 14
Q-Code 14 signals a memory-related initialization problem. It typically means an issue with RAM settings, placement, or compatibility. Checking the RAM’s position, clearing the CMOS, or updating the BIOS can help fix startup problems linked to this code.
Gene-Z Code 19
Code 19 suggests an issue during early CPU or memory setup on Gene-Z motherboards. It may be caused by incorrect memory installation or an outdated BIOS. Reseating the RAM and updating the BIOS often solve this problem.
Q-Code 12, 54, 55 on Asus Z690-E
On the Asus Z690-E motherboard, Q-Code 12 indicates an early initialization issue, 54 signals memory problems, and 55 means the RAM is undetected. Checking RAM seating, compatibility, or updating the BIOS can help fix these errors.
Motherboard Stuck On CPU Initialization screen
If your motherboard is stuck on the CPU initialization screen, it likely means an issue with the CPU or RAM. Try reseating the CPU, checking power connections, or updating the BIOS to resolve the problem.
New Error 15 When Booting Gigabyte Motherboard
Error 15 on a Gigabyte motherboard usually means a memory issue during pre-initialization. Ensure your RAM is properly seated, try different slots, or update the BIOS to fix booting problems.
Asus Strix x570 -E gaming Q Code Error 36 No post
Q Code 36 on the Asus Strix X570-E means a CPU initialization failure. Improper CPU installation, outdated BIOS, or incompatible RAM can cause it. Check the CPU socket, update BIOS, and test with a single RAM stick.
CPU Post Memory Initialization Error 36
Error 36 appears when the CPU fails to initialize after memory setup. This might be due to a BIOS issue or unstable overclocking settings. Resetting BIOS to default and verifying hardware connections can often resolve this error.
Pre Memory CPU initialization CPU module specific MSI
On MSI motherboards, pre-memory CPU initialization issues can be caused by a faulty CPU, RAM, or outdated BIOS. Try reseating components, resetting CMOS, and updating BIOS to fix compatibility problems and ensure smooth booting.
CPU Post Memory initialization boot Strap Processor (BSP) selection
During post-memory initialization, the system selects the Bootstrap Processor (BSP) to handle critical startup tasks. If errors occur, it may indicate CPU or BIOS-related issues. Updating BIOS and checking CPU seating can help resolve problems.
Error Code 15 pre-memory system agent initialization is started?
Error 15 means the system agent is initializing before memory is fully configured. Unstable memory settings or BIOS issues can cause this. Resetting CMOS and ensuring RAM compatibility can often fix the problem.
Z87X OC Code 15: Pre-memory North-Bridge initialization is started.

On Z87X OC motherboards, Code 15 signals the North Bridge is initializing pre-memory. If stuck, it may be due to a faulty CPU or RAM. Try resetting CMOS, updating BIOS, and checking component compatibility.
Q Code 15 (Pre-memory System Agent initialization is started
Q Code 15 means the pre-memory system agent is initializing. If your system doesn’t proceed, the issue may be related to RAM or BIOS settings. Clearing CMOS, reseating RAM, and updating BIOS are common fixes.
PC not starting – POST “Memory initialization error occurs” – RAM only working a one bank
One RAM bank might be faulty if your PC fails to start and shows a memory initialization error. Try reseating the RAM, testing different slots, or updating the BIOS. A defective motherboard or incompatible RAM could also be the issue.
FAQs
1. What Does Pre-Memory CPU Initialization Is Started Mean?
This means that the CPU is being prepared before accessing memory. This step ensures smooth communication between the processor and other components for a successful system startup.
2. What Does CPU Post Memory Initialization Mean?
This step happens after the memory is active. It configures advanced CPU settings, ensuring stability and optimizing system performance for a smooth and efficient boot process.
3. What Is CPU Initialization?
CPU initialization prepares the processor for operation by setting up essential hardware, including memory controllers and caches, to ensure proper system functionality.
4. What Does 15 Mean on a Motherboard?
Motherboard code 15 usually signals a pre-memory initialization issue, often related to RAM or CPU setup. Checking memory seating and updating BIOS may help.
5. Can RAM Cause Random Restarts?
Yes, faulty or incompatible RAM can cause sudden system restarts. Cleaning RAM slots, reseating sticks, or replacing defective modules can fix the issue.
6. What Is the Meaning of Memory Initialization?
Memory initialization sets up RAM for proper communication with the CPU, ensuring data can be read and written correctly for smooth performance.
7. What Happens When a CPU Starts?
The CPU initializes essential hardware, loads firmware (BIOS/UEFI), and prepares memory and storage for system boot-up, ensuring stable operation.
8. What Is the CPU Out of Memory Error?
This error happens when the CPU runs out of available memory, often due to excessive programs running or insufficient RAM. Closing apps or upgrading RAM helps.
9. How Is RAM Initialized?
The system checks, configures, and assigns memory resources during startup to ensure stability and efficient performance. This process prevents crashes and data corruption.
10. What Is CPU Register Memory?
CPU registers are small, ultra-fast memory units inside the processor. They store temporary data and instructions, helping the CPU execute tasks quickly.
Conclusion
Pre-memory CPU initialization is a crucial step in your computer’s startup process. It ensures that the CPU, memory, and other critical components are ready for action, preventing errors and ensuring smooth system operation. Understanding this process helps you troubleshoot issues like boot failures or performance problems. If you’re experiencing issues like error codes or a stuck initialization screen, checking components like RAM and BIOS settings can often resolve the problem. Ensuring proper pre-memory initialization guarantees a faster, more reliable, and secure computing experience.