Understanding VDDCR CPU voltage is key for anyone looking to get the most out of their processor.
VDDCR CPU voltage refers to the voltage supplied to the CPU core, influencing performance and stability. Typically ranging from 1.350 to 1.375 volts, it is key in managing power and temperature for optimal performance.
In this guide, we’ll break down VDDCR CPU voltage, explain why it matters, explain how to adjust it and provide best practices for keeping your hardware safe while maximizing performance. Let’s dive into the details!
Understanding Vddcr CPU Voltage
1. Factors Influencing Vddcr CPU Voltage
Your CPU model, motherboard, cooling, and overclocking impact VDDCR CPU Voltage. Higher speeds need more power, but too much can cause overheating or damage. Balance is key.
2. Monitoring and Adjusting Vddcr CPU Voltage
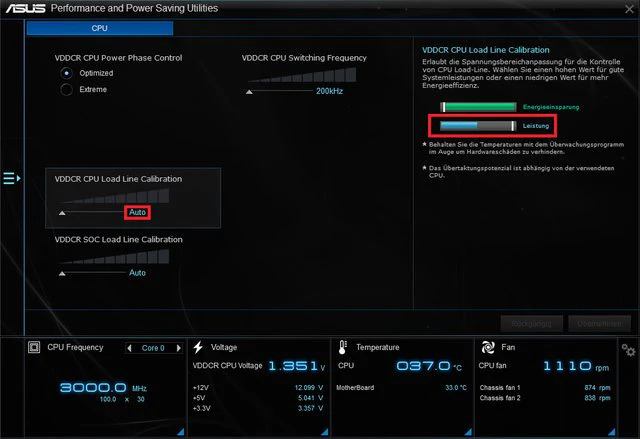
You can check and change VDDCR CPU Voltage using BIOS or software like Ryzen Master. Adjusting it carefully improves performance, prevents crashes, and keeps temperatures low.
The Importance of VDDCR CPU Voltage
The VDDCR CPU voltage plays a pivotal role in several aspects of computer performance:
- Performance Optimization: Adjusting the VDDCR CPU voltage can enhance the CPU’s performance. For instance, increasing the voltage can support higher clock speeds during overclocking, leading to improved computational capabilities.
- System Stability: Proper voltage settings ensure that the CPU operates without errors. Incorrect voltage levels can lead to system instability, causing crashes or unexpected behavior.
- Thermal Management: Voltage adjustments influence the heat generated by the CPU. Higher voltages can increase temperatures, necessitating efficient cooling solutions to maintain safe operating conditions.
What is VDDCR CPU Voltage?
VDDCR CPU Voltage is the power supply to your CPU, helping it function properly. It controls performance, stability, and heat.
Setting it too high causes overheating, while too low can crash your system. Proper adjustment ensures smooth and efficient operation.
Why Does VDDCR CPU Voltage Matter?
1. Stability and Performance:
Proper voltage ensures your CPU runs smoothly without crashes or slowdowns. Too much or too little can cause instability, freezing, or unexpected shutdowns during heavy tasks.
2. Overclocking:
Overclocking pushes your CPU faster, but it needs extra voltage for stability. Too much can overheat your system, while too little can cause performance drops or crashes.
3. Temperature Management:
Higher voltage generates more heat, requiring better cooling. Managing voltage properly keeps your CPU cool, extends life, and prevents thermal throttling or hardware damage.
How Does VDDCR CPU Voltage Work?
1. Regulation:
The motherboard’s power system controls and stabilizes CPU voltage. It adjusts power delivery to match performance needs, preventing sudden spikes or drops that could harm your CPU.
2. BIOS Settings:
You can adjust VDDCR CPU Voltage in your BIOS/UEFI. Manufacturers provide auto settings, but advanced users can fine-tune voltage to improve stability, performance, or power efficiency.
3. Monitoring:
Monitoring voltage helps prevent overheating and instability. Tools like HWMonitor, Ryzen Master, or BIOS readings help track voltage levels to ensure safe CPU operation.
The Role of VDDCR CPU Voltage in Overclocking
VDDCR CPU Voltage is key to stable overclocking. Increasing voltage helps your CPU run faster, but too much causes overheating. Proper tuning balances performance and temperature, ensuring smooth operation without crashes or reducing the CPU’s lifespan.
Tips for Managing VDDCR CPU Voltage:
1. Understand Your CPU:
Every CPU has a safe voltage range. Learn your processor’s limits before adjusting settings to avoid overheating, crashes, or long-term damage.
2. Start Conservatively:
When tweaking voltage, make small changes. Sudden high adjustments can cause overheating, while lowering it too much may result in instability and random shutdowns.
3. Monitor Temperatures:
Always check CPU temperatures after adjusting the voltage. Keeping temperatures safe prevents performance loss, system crashes, and long-term damage.
4. Use Reliable Software:
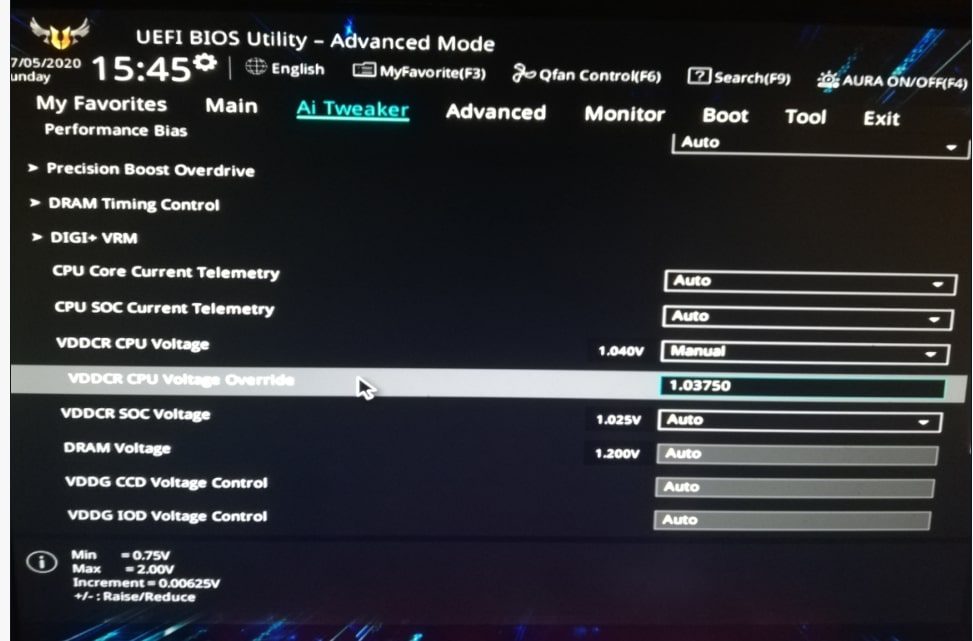
Use trusted software like HWMonitor, HWiNFO, or Ryzen Master to track voltage and temperatures accurately, ensuring your CPU stays within safe limits.
5. Seek Expert Advice:
If unsure, check forums and guides or consult experienced users. Following expert recommendations helps you safely manage CPU voltage without risking damage.
The Basics.
1. What is a VRM?
A voltage regulator module (VRM) controls the CPU’s power. It ensures stable voltage, preventing damage and keeping performance smooth, especially during high workloads or overclocking.
2. What is the difference between Ryzen and Zen?
Zen is the architecture that powers Ryzen CPUs. Ryzen is the product line, while Zen defines how the chips are designed for better speed, efficiency, and performance.
3. What is AMD CBS?
AMD CBS (Custom BIOS Settings) is an advanced menu in the BIOS. It allows users to tweak CPU, memory, and power settings for better performance or stability.
4. What is PBO?
Precision Boost Overdrive (PBO) is an AMD feature that pushes CPU speeds higher when cooling allows. It boosts performance automatically beyond standard limits.
5. What are safe voltages for Ryzen APU internal GPU?
For most Ryzen APUs, a safe GPU voltage is between 1.1V and 1.2V. Higher voltages can increase performance but may cause overheating or shorten lifespan.
6. What are safe voltages for Ryzen SoC?
A safe SoC voltage for Ryzen is typically around 1.0V to 1.2V. Going too high can cause instability, overheating, or damage to system components.
7. What are safe voltages for Ryzen CPUs?
Safe CPU voltages for Ryzen range from 1.2V to 1.35V. Higher voltages can improve performance but may lead to excess heat and a shorter CPU lifespan.
BIOS Settings.
1. What is VDDCR CPU Load Line Calibration?
Load Line Calibration (LLC) adjusts voltage drop under load, keeping the CPU stable. It prevents crashes during heavy tasks or overclocking by balancing power delivery.
2. What is VDDCR CPU Current Capability?
This setting controls how much current the CPU can draw. Higher values support overclocking but may increase heat and power consumption.
3. What is VDDCR CPU Switching Frequency?
It determines how fast power phases switch. Higher frequencies improve stability but can increase heat, while lower values reduce power consumption.
4. What is VDDCR CPU Power Duty Control?
This setting manages how power phases share the load. It helps balance efficiency, stability, and performance, especially when overclocking.
5. What is VDDCR CPU Power Phase Control?
It optimizes power delivery by adjusting how many power phases are active. More phases improve stability but may increase heat and power usage.
6. What is SOC?
The System on Chip (SoC) controls memory, PCIe, and integrated graphics. It’s essential for stability, especially in Ryzen APUs.
7. What is VDDCR SOC Load Line Calibration?
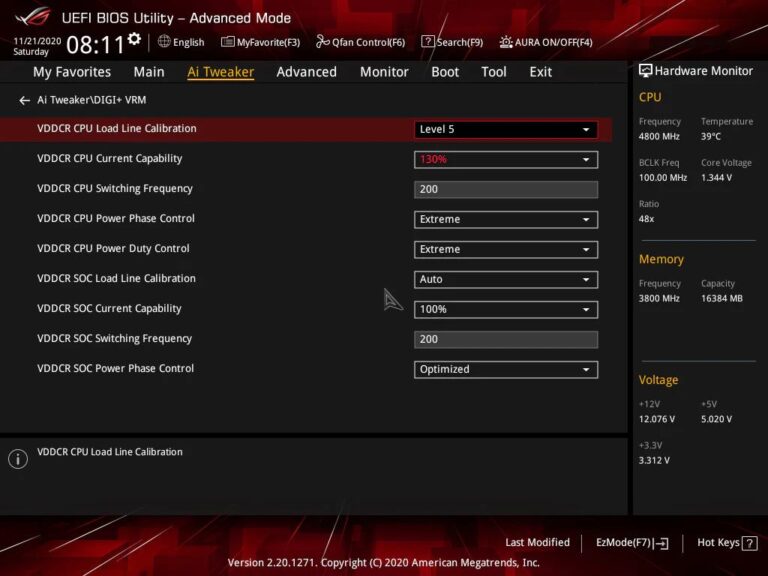
Like CPU LLC, this setting stabilizes voltage for the SoC, preventing drops that could cause instability in memory and PCIe devices.
8. What is VDDCR SOC Current Capability?
It adjusts how much current the SoC can handle. Higher values improve stability under heavy loads but may increase power draw and heat.
9. What is VDDCR SOC Switching Frequency?
This controls how often the SoC power phases switch. Higher settings enhance stability, while lower ones reduce power consumption.
10. What is VDDCR SOC Power Phase Control?
It manages how many SoC power phases are active, balancing efficiency and stability based on workload needs.
11. What is VDDCR SOC Voltage?
It’s the power supplied to the SoC. Safe ranges are usually 1.0V to 1.2V, with higher values affecting stability and temperature.
12. What is CPU Core Ratio?
The CPU Core Ratio controls clock speed by multiplying the base frequency. Higher ratios increase performance but may require more voltage.
13. What is FCLK?
Fabric Clock (FCLK) links the CPU and Infinity Fabric. A 1:1 ratio with a memory clock improves performance and reduces latency.
14. What is the GFX clock frequency?
It’s the speed of the integrated GPU in an APU. Higher frequencies improve graphics performance but need better cooling.
15. What is the GFX core voltage?
This is the power supplied to the integrated GPU. Too much voltage can cause overheating, while too little may cause instability.
16. What is AMD SAM?
Smart Access Memory (SAM) allows the CPU to fully access GPU memory, boosting gaming performance by reducing bottlenecks.
17. What is DRAM Voltage?
It controls the power sent to RAM. Safe values are typically 1.2V to 1.35V, with overclocking requiring more voltage.
18. What is Global C-State Control?
This setting manages power-saving CPU sleep states. Enabling it can reduce power use, while disabling it may improve stability in some workloads.
Considerations When Adjusting Voltage
While adjusting the VDDCR CPU voltage can yield performance benefits, it’s essential to proceed with caution:
- Monitor Temperatures: Higher voltages can lead to increased heat output. Ensure your cooling system is adequate to handle the additional thermal load.
- Incremental Changes: Make small adjustments and test system stability after each change. This approach helps identify the optimal voltage without compromising system integrity.
- Understand the Risks: Excessive voltage can degrade the CPU over time, reducing its lifespan. Always refer to manufacturer guidelines and community resources for safe voltage ranges.
Adjusting VDDCR CPU Voltage in BIOS/UEFI
In the BIOS/UEFI, you can adjust the VDDCR CPU voltage to fine-tune performance. This is especially useful for overclocking or stabilizing your system. Always adjust carefully to avoid overheating.
Safe Voltage Levels: Protecting Your Hardware
To protect your hardware, keep VDDCR CPU voltage within safe ranges. Exceeding safe levels can lead to overheating, instability, or permanent damage. Ensure proper cooling for higher voltage settings.
What is VDDCR CPU Voltage vs Core Voltage?
VDDCR CPU voltage supplies power to the CPU, while core voltage refers to the voltage for individual CPU cores. VDDCR is often used interchangeably with core voltage but is technically different.
What is VDDCR CPU Voltage Offset Mode?
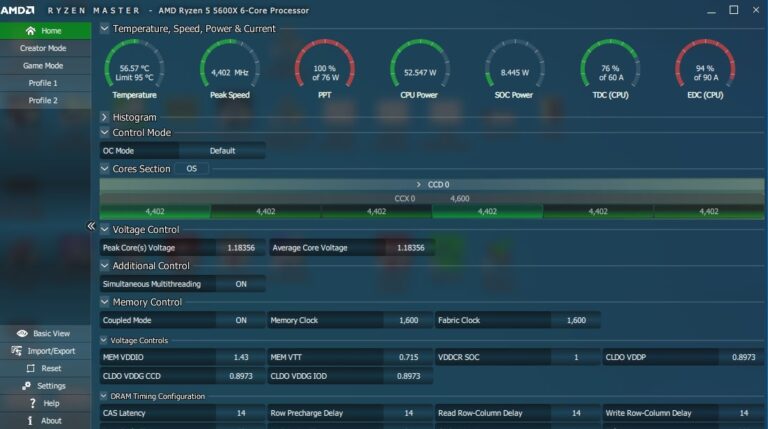
Offset mode adjusts VDDCR CPU voltage based on a reference value. It allows for fine control, reducing voltage when the system is idle and increasing it under load for stability or overclocking.
What is VDDCR CPU Voltage Ryzen?
VDDCR CPU voltage in Ryzen CPUs controls power delivery to the CPU cores. Ryzen processors operate at lower voltage ranges for energy efficiency while maintaining good performance and stability.
VDDCR CPU Voltage Override
VDDCR CPU voltage override sets a fixed voltage value, overriding automatic adjustments. This is useful for overclocking but increases heat and power consumption, so proper cooling is essential.
What is VDDCR CPU Voltage Ryzen 7?
VDDCR CPU voltage for Ryzen 7 processors typically ranges from 1.2V to 1.4V under load. Adjusting this voltage can improve performance but may increase heat output, requiring good cooling solutions.
VDDCR CPU vs SoC Voltage
VDDCR CPU voltage powers the CPU cores, while SoC voltage powers other components like the memory controller and integrated graphics. Both voltages are essential but serve different functions for stable operation.
VDDCR CPU Voltage Undervolt
Undervolting VDDCR CPU voltage reduces the power supplied to the CPU, lowering temperatures and power consumption. This can improve efficiency but may reduce performance if done too aggressively.
VDDCR CPU Offset Voltage
VDDCR CPU offset voltage adjusts the base voltage by a set amount, either increasing or decreasing. This is useful for fine-tuning stability without making large voltage changes.
CPU VDDCR_VDD and VDDCR_SOC
VDDCR_VDD powers the CPU core, while VDDCR_SOC supplies power to the System-on-chip (SoC) components. Both are critical for system stability but serve different parts of the CPU.
Overclocking Ryzen: SOC Voltage?
For overclocking Ryzen, adjusting the SoC voltage is crucial for stability, especially when increasing memory speeds or utilizing integrated graphics. It helps ensure the SoC remains stable under higher workloads.
Ryzen Master VDDCR SOC Voltage Question
In Ryzen Master, VDDCR SOC voltage can be adjusted to ensure stability during overclocking. Increasing it can improve memory and PCIe stability, but high voltages require adequate cooling.
VDDCR CPU Voltage Does Not Match Core Voltage
VDDCR CPU voltage doesn’t always match core voltage, as it represents the overall power supplied to the CPU. Core voltage, on the other hand, is specific to each core’s needs. Both are related but separate.
SoC vs VDDCR SoC?
SoC (System on Chip) powers components like memory and integrated graphics. VDDCR SoC refers to the specific voltage that powers these SoC components. Both are essential but affect different parts of the system.
High or Normal VDDR SOC Voltage?
High VDDR SOC voltage can improve stability for memory overclocking, but it generates more heat. Normal voltage is safer for everyday use, while high voltage is better for extreme performance but requires good cooling.
Ryzen 9 3900X VDDCR CPU and VDDCR SOC Voltage
The Ryzen 9 3900X uses around 1.2-1.35V for VDDCR CPU voltage. VDDCR SOC voltage is generally lower, around 1.1V to 1.2V, depending on your setup and usage conditions for stability.
3900X VDDCR (CPU Power)
The VDDCR CPU power for the Ryzen 9 3900X refers to the voltage supplied to the CPU cores. It typically ranges between 1.2V and 1.35V for stability and performance under load.
How to Change the VDDCR CPU Voltage
To change VDDCR CPU voltage, access the BIOS/UEFI and adjust the CPU voltage settings. Use caution when increasing the voltage, which impacts power consumption and heat levels.
VDDCR CPU Voltage Offset Mode Or Auto
VDDCR CPU voltage is manually adjusted above or below default values in offset mode. Auto mode allows the system to automatically set the voltage based on CPU demands, balancing performance and efficiency.
VDDCR CPU Voltage ignored BIOS B550-E
If the VDDCR CPU voltage is ignored in the BIOS on a B550-E motherboard, check for BIOS updates or reset settings. This can happen due to system limitations or incorrect configurations.
VDDCR CPU Voltage vs Core Voltage In Bios Ryzen 5

VDDCR CPU voltage controls the power for the entire CPU, while core voltage specifically targets the individual CPU cores. Both can be adjusted separately for overclocking or stability in BIOS settings.
Question about RAM voltage and CPU Voltage
RAM voltage and CPU voltage are separate. RAM voltage affects the memory, while CPU voltage affects the processor. Both need to be balanced for optimal performance, especially during overclocking.
Ryzen 5000, difference between VDDCR and Curve Optimizer?
VDDCR refers to the voltage provided to the CPU cores, while the Curve Optimizer adjusts the CPU’s performance curve to optimize efficiency and performance. Both work together for better CPU management.
FAQs
1. What does VDDCR mean?
VDDCR stands for “Voltage for Direct Current to CPU Regulator.” It controls the power supplied to the CPU cores.
2. What is a good VDDCR CPU voltage?
A good VDDCR CPU voltage is typically between 1.2V and 1.35V, ensuring stable performance without excessive heat.
3. What voltage should CPU be at?
The CPU voltage should be around 1.1V to 1.4V, depending on the specific model and overclocking preferences.
4. Is 1.4 volts safe for CPU?
1.4 volts can be safe for short-term overclocking, but consistent use at that voltage can increase the risk of damage.
5. What is the max voltage for CPU VDDQ?
The maximum voltage for CPU VDDQ is typically around 1.2V to 1.35V, depending on the CPU model and system requirements.
Conclusion
In conclusion, VDDCR CPU voltage plays a vital role in your processor’s performance, stability, and temperature management. Proper adjustments ensure smooth operation, prevent overheating, and safeguard your hardware, especially during overclocking. Always monitor and adjust carefully for optimal results.